//栈溢出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int vulfun(char *str)
{
char stack[10];
strcpy(stack,str);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
char *str="AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA";
vulfun(str);
return 0;
}
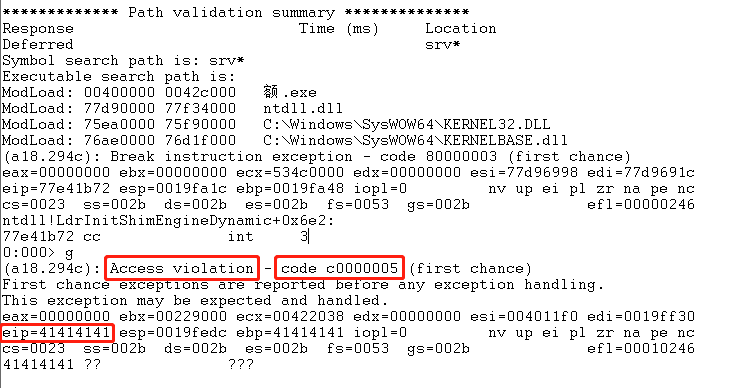
//堆溢出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<Windows.h>
int main()
{
HANDLE hHeap;
char *heap;
char str[]="AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA";
hHeap=HeapCreate(HEAP_GENERATE_EXCEPTIONS,0X1000,0XFFFF);
getchar();
heap=HeapAlloc(hHeap,0,0X10);
printf("heap address:%p\n",heap);
strcpy(heap,str);
HeapFree(hHeap,0,heap);
HeapDestroy(hHeap);
return 0;
}
//基于栈的整数溢出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
int i;
char buf[8];
unsigned short int size;
char overflow[65550];
memset(overflow,65,sizeof(overflow));
printf("请输入数值");
scanf("%d",&i);
size=i;
printf("%d\n",size);
printf("%d\n",i);
if(size>8)
{
return -1;
}
memcpy(buf,overflow,i);
return 0;
}
//基于堆的整数溢出
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <windows.h>
int main()
{
int *heap;
unsigned short int size;
char *pheap1,*pheap2;
HANDLE hHeap;
printf("请输入size数值:\n");
scanf("%d",&size);
hHeap=HeapCreate(HEAP_GENERATE_EXCEPTIONS,0X100,0XFFF);
if(size<=0X50)
{
size-=5;
printf("size:%d\n",size);
pheap1=HeapAlloc(hHeap,0,size);
pheap2=HeapAlloc(hHeap,0,0X50);
}
HeapFree(hHeap,0,pheap1);
HeapFree(hHeap,0,pheap2);
return 0;
}
//格式化字符串漏洞
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char buff[1024];
strncpy(buff,argv[1],sizeof(buff)-1);
printf(buff);
return 0;
}
//双重释放漏洞
#include<stdio.h>
#include<Windows.h>
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
void *p1,*p2,*p3;
p1=malloc(100);
printf("p1=%p\n",p1);
p2=malloc(100);
printf("p2=%p\n",p2);
p3=malloc(100);
printf("p3=%p\n",p3);
printf("free p1\n");
free(p1);
printf("free p2\n");
free(p2);
printf("free p3\n");
free(p3);
printf("double free p2\n");
free(p2);
return 0;
}
//释放重引用漏洞
#include<stdio.h>
#define size 32
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
char *buf1,*buf2;
buf1=(char*)malloc(size);
printf("buf1=%p\n",buf1);
free(buf1);
buf2=(char*)malloc(size);
printf("buf2=%p\n",buf2);
memset(buf2,0,size);
printf("buf2:%d\n",buf2);
strncpy(buf1,"XXXX",5);
printf("buf2:%s\n",buf1);
free(buf2);
return 0;
}
//数组越界访问漏洞
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int index;
int arr[3]={111,222,333};
printf("输入数组索引下标:");
scanf("%d",&index);
printf("数组元素为:%d\n",arr[index]);
arr[index]=1;
return 0;
}
